News
Wie gestalten wir den digitalen Euro als neues Medium der Kooperation?
Mit Sebastian Gießmann (Universität Siegen. SFB 1187) und Petra Gehring (TU Darmstadt)
Sebastian Gießmann und Petra Gehring diskutieren am 26. Mai auf der diesjährigen re:publica über den digitalen Euro, seine Zukunft und Kontroversen. Das re:publica Festival widmet sich Themen der digitalen Gesellschaft.
Über den Beitrag
2025 wird ein entscheidendes Jahr für den digitalen Euro. Die Europäische Zentralbank steckt mitten in der Vorbereitungsphase für diese neue Form des Bargelds. Währenddessen stockt der nötige politische Prozess in Brüssel. Dabei ist das Projekt immer noch vielen Bürger:innen unbekannt: Im Juni 2024 wussten 59 Prozent der Deutschen nichts über die digitale Zentralbankwährung. Und wer schon davon gehört hat, vermutet vieles – angefangen bei der (keinesfalls geplanten) Abschaffung von Schein und Münze, befürchteter finanzieller Überwachung bis zur Einführung einer europäischen Kryptowährung.
Wenn wir ein neues Geld der europäischen Öffentlichkeit bis 2028 realisieren wollen, braucht es deshalb vor allem: mehr zivilgesellschaftliche Aufmerksamkeit für die digitale Zentralbankwährung, mehr und genaueres Wissen, mehr Deliberation und zivilisierten Streit, mehr Kooperation, kollektives Vorstellungsvermögen und politischen Willen. Die Philosophin Petra Gehring und der Medientheoretiker Sebastian Gießmann debattieren mit Euch, wie wir den digitalen Euro unter den aktuellen Bedingungen für alle Generationen gestalten können, und müssen.
Sebastian Gießmann und Petra Gehring diskutieren über den digitalen Euro, seine Zukunft, seine Kontroversen, seine politische Philosophie, Medientheorie und Ökonomie. Alle Generationen brauchen digital cash. Aber wie gestalten wir als europäische Zivilgesellschaft ein neues Medium der Kooperation?
Die Session „Das neue Geld der europäischen Öffentlichkeit: Wie gestalten wir den digitalen Euro?“ findet am 26. Mai von 13.45-14.15 Uhr statt. Weitere Details hier →
Über die re:publica
Die re:publica ist ein Festival für die digitale Gesellschaft und die größte Konferenz ihrer Art in Europa. Die Teilnehmer*innen der re:publica bilden einen Querschnitt der (digitalen) Gesellschaft. Zu ihnen gehören Vertreter*innen aus Wissenschaft, Politik, Unternehmen, Hackerkulturen, NGOs, Medien und Marketing sowie Blogger*innen, Aktivist*innen, Künstler*innen und Social Media-Expert*innen. Die re:publica 25 fand vom 26.-28. Mai 2025 in Berlin statt. Sie steht unter dem Motto “Generation XYZ “.
Die aktive Beteiligung der Community – initiiert durch den dem Festival vorausgehenden “Call for Participation” – macht die re:publica zu diesem einzigartigen Event. Jede*r Interessierte reicht spannende Themen, Ideen oder Projekte ein, die damit selbst Teil des Programms werden können. Unter anderem dadurch erreicht die re:publica eine hohe Themendiversität und außergewöhnliche Vernetzungsmöglichkeiten. Über 50 Prozent der re:publica-Sprecher*innen sind weiblich. Damit ist die re:publica seit langem Vorreiter und wegweisend in der Debatte rund um die Themen “Gender Balance” und “Diversity” im Allgemeinen.
Im Jahr 2007 von Tanja Haeusler, Andreas Gebhard, Markus Beckedahl und Johnny Haeusler gegründet, engagieren sich die Gesellschafter*innen der republica GmbH seit über einem Jahrzehnt in den Bereichen Netzpolitik, Digitalkultur und digitale Gesellschaft.
Über die Forschenden
Sebastian Gießmann ist Akademischer Oberrat am Seminar für Medienwissenschaften an der Universität Siegen. Er ist Teilprojektleiter des Teilprojekts „A01 – Digitale Netzwerktechnologien zwischen Spezialisierung und Generalisierung“ im DFG-geförderten Sonderforschungsbereich 1187 „Medien der Kooperation“.
Petra Gehring ist Professorin für Philosophie an der TU Darmstadt. Sie arbeitet zu einem breiten Spektrum von Themen, von der Geschichte der Metaphysik bis hin zur Technikforschung und zu den Methoden der Digital Humanities. Sie war u. a. Fellow am Wissenschaftskolleg zu Berlin und ist derzeit Vorsitzende des Rats für Informationsstrukturen der gemeinsamen Wissenschaftskonferenz von Bund und Ländern sowie Direktorin des Zentrums verantwortungsbewusste Digitalisierung.
[/one_half]
Stellenausschreibung:
SHK/WHB-Stelle im SFB-Teilprojekt A04
Für das Teilprojekt A04 „Normale Betriebsausfälle. Struktur und Wandel von Infrastrukturen im öffentlichen Dienst“ im Sonderforschungsbereich 1187 „Medien der Kooperation“ suchen wir eine studentische Hilfskraft (SHK) (m/w/d) oder eine wissenschaftliche Hilfskraft mit Bachelor-Abschluss (WHB) (m/w/d) zum 01. Juni zu folgenden Konditionen:
- 9 Wochenstunden
- Befristet für 16 Monate
- Beschäftigung auf Grundlage des Wissenschaftszeitvertragsgesetzes
Ihre Aufgaben:
- Erbringung wissenschaftlicher Hilfstätigkeiten
- Unterstützung bei der Forschung sowie bei der Planung von Tagungen und Workshops
- Literaturrecherche und -beschaffung
- Einpflegen bibliografischer Angaben
- Mitarbeit bei der Datenaufbereitung und -auswertung
- Pflege der Projektwebsite
Ihr Profil:
- Immatrikulation im Studiengang BA oder MA Sozialwissenschaften oder Medienwissenschaften mit sozialwissenschaftlichem Schwerpunkt
- Interesse an einer Tätigkeit im wissenschaftlichen Umfeld
- Sicherer Umgang/selbstständiges Arbeiten mit MS-Office
- Strukturiertes Arbeiten, Freude an Teamarbeit, Eigeninitiative und Verantwortungsbewusstsein
➔ vollständige Stellenausschreibung
Wir freuen uns auf Ihre Bewerbung bis zum 30.04.2025.
Weitere Infos zu dem Projekt erhalten Sie hier: https://www.mediacoop.uni-siegen.de/de/projekte/a04/
Ihre Ansprechperson:
Damaris Lehmann, M.A.
damaris.lehmann[æt]uni-siegen.de
A workshop report (February 4-7)
In February 2025, the Mixing Methods Winter School at the Collaborative Research Centre 1187 brought together over thirty participants, including international researchers, students, and experts from various disciplines. The program combined hands-on experimentation with critical inquiry into AI-driven research methods. Throughout the Winter School, participants critically engaged with AI not just as a tool but as a collaborator, reflecting on its role in shaping the research process.
The week opened with a keynote by Jill Walker Rettberg from the University of Bergen, who introduced “Qualitative Methods for Analyzing Generative AI: Experiences with Machine Vision and AI Storytelling.” Her talk set the stage for discussions on how qualitative inquiry can reveal the underlying narratives and biases in AI-generated content.
Participants then engaged in two hands-on workshops designed to explore mixed techniques for probing and prompting AI models. Carlo de Gaetano (Amsterdam University of Applied Sciences), Andrea Benedetti, and Riccardo Ventura (Density Design, Politecnico di Milano) led the workshop “Exploring TikTok Collections with Generative AI: Experiments in Using ChatGPT as a Visual Research Assistant,” examining how AI can assist in visual analysis of networked video content. Together with Elena Pilipets (University of Siegen) and Marloes Geboers (University of Amsterdam) participants then explored the semantic spaces and aesthetic neighborhoods of synthetic images generated by Grok during the workshop “Web Detection of Generative AI Content”.
After an introductory first day, the Winter School shifted its focus to two in-depth project tracks. The first project, “Fabricating the People: Probing AI Detection for Audio-Visual Content in Turkish TikTok,” explored how protesters and the manosphere engage with cases of gender-based violence on Turkish TikTok and how these videos can be studied using different AI methods. The second project, “Jail(break)ing: Synthetic Imaginaries of ‘Sensitive’ AI,” explored how AI models reframe sensitive topics through generative storytelling under platform-imposed restrictions.
The recaps of the projects are:
Fabricating the People: Probing AI Detection for Audio-Visual Content in Turkish TikTok
Facilitated by Sara Messelaar Hammerschmidt, Lena Teigeler, Carolin Gerlitz and Duygu Karatas (all University of Siegen)
The project explored video shorts from the Turkish manosphere – content centered on masculinity, gender dynamics, and “men’s rights” issues that often discuss dating, self-improvement, and family life. While this content is found on mainstream platforms and passes moderation, it still frequently veers into misogynistic or even violent rhetoric. Our project explored AI-assisted methods to make sense of large amounts of this contentious multimodal data.
Rationale
Specifically, we set out to develop methods to map how video shorts may become a vehicle for the ambient amplification of extremist content across platforms. We explored two approaches using off-the-shelf multimodal large language models (LLMs). The first sought to extend the researcher’s interpretation of how manosphere content addresses bodies, which are both performed and contested intensely across the issue space. We did this by implementing few-shot labelling of audio transcriptions and textual descriptions of videos. The second method sought to interrogate the role of generative AI in (re)producing memes, genres, and ambience across video shorts. We achieved this by experimenting with zero-short descriptions of video frames to describe detected genres, formats and the possible use of AI in video production processes.
Methods and Data
We started with a period of “deep hanging out” in Turkish manosphere and redpill spaces on Tiktok, Youtube, and Instagram. We identified prominent accounts and crawled them to build a data sample of 3600 short videos from across the three platforms. Several analyses were carried out before the Winter School. These included metadata scraping, video downloading, scene detection, scene collage creation. transcribing audio, and directing an LLM to generate video descriptions following Panofsky’s a three-step iconological method, which differentiates between pre-iconographic analysis (recognizing fundamental visual elements and forms), iconographic analysis (deciphering symbols and themes within their cultural and historical contexts), and iconological interpretation (revealing deeper meanings, ideologies, and underlying perspectives embedded in the image) (Panofsky, 1939).
Method one: Video shorts continue to grow in popularity and prominence across social media platforms, building out new gestural infrastructures (Zulli and Zulli, 2022) and proliferating ambient images (Cubitt et al., 2021). Qualitatively investigating this rich multimodal content at a scale that highlights the broader atmospheres and cultures developed through algorithmic circulation is challenging. Multimodal LLMs have the potential to extend researcher’s ethnographic coding capacity to larger datasets and to account for more varied formats than ever before (Li and Abramson, 2023). We therefore investigate possibilities for using cutting-edge multimodal LLMs for qualitative coding of multimodal data as a methodology for qualitatively investigating ambience and amplification in video-short-driven algorithmic media.
We began with a qualitative ethnographic immersion in our dataset, watching the videos and developing a codebook that described how the videos related to our interest in how bodies were both performatively and discursively addressed. We applied our codebook manually to the textual data the LLM allowed us to produce out of the videos, i.e., not only the metadata, but also audio transcriptions and LLM-generated video Panofskian descriptions. After the codebook stabilized, we applied it to a random subset of 150 datapoints. We then developed a few-shot learning script that applied these labels to the entire dataset. We chose three examples to belong to a labelling “core” and then programmed a script to sample dynamically from the rest of our 150 datapoints to include as many further examples as could be accommodated by the context window limitation. We then prompted the LLM to apply our labels to the entire dataset. This let us explore extending the researcher’s qualitative insights to larger, multimodal data.
During the codebook development and coding process, the Panofsky descriptions brought the visual prominence of hands and hand gestures across the dataset to our attention. We therefore also applied a separate process to our data to begin isolating hands for closer investigation.
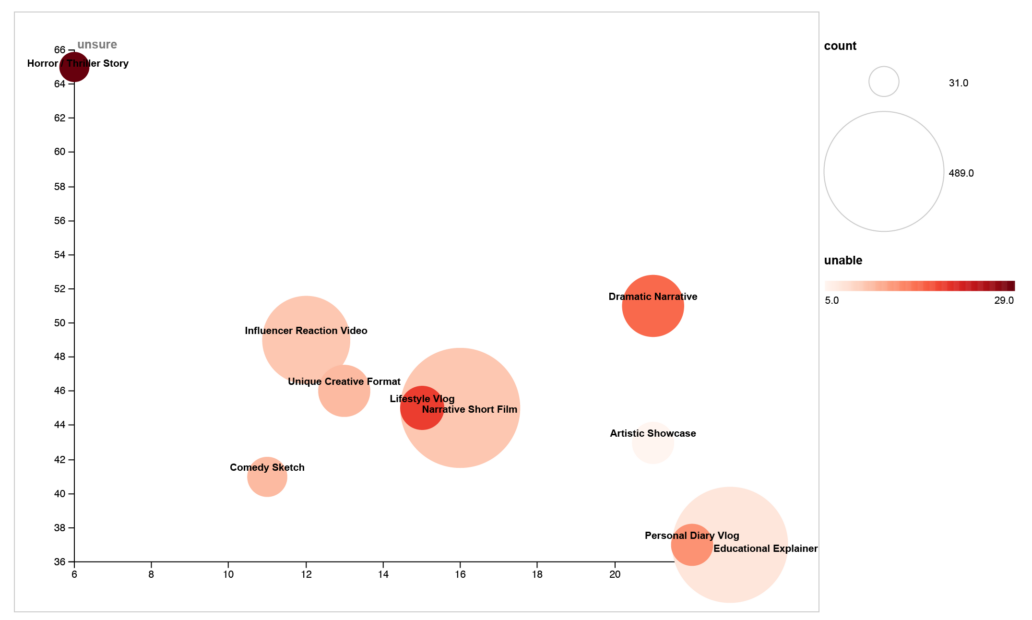
Method two: Automation technologies and generative AI play an increasingly prominent role in the creation of audio-visual social media content. This ranges from image or video generation, to AI voice-over production, to video editing, content cropping, platform optimization, and beyond (Anderson and Niu, 2025). Detecting these production methods, however, is challenging. Even state-of-the-art machine-learning struggles to analyze multimodal media (Bernabeu-Perez, Lopez-Cuena and Garcia-Gasulla, 2024). We set out to find qualitative alternatives for exploring the role of AI aesthetics in video short production. Therefore, we proceeded with a twofold approach, developed within an iterative process of prompt engineering: First, we asked the LLM to create a structured visual analysis of a social media video collage by evaluating its composition, camera techniques, editing style, mise-en-scène, text overlays, genre, and platform-specific features, summarizing key characteristics as a tag list. This initial prompt helped distinguish between different video formats and styles, identifying those that are particularly likely to incorporate automation or AI-driven edits. Second, we directly instructed the LLM to assess the likelihood that AI was used in the production of this video. In this way, we set out to explore “popular” AI’s role in both the creation and the interpretation of misogynistic video-shorts.
Research questions
- How can AI-based methods be used to extend ethnographic research into networked digital cultures?
- How can these methods help increase researcher sensitivity to phenomena that happen at network scale, for example, ambient amplification practices?
- Can AI identify and characterize synthetic content? How does AI see AI?
- As an approximation of that question, how does AI interpret and distinguish between different content genres and formats?
Key findings
Our work demonstrated the extent to which the internal cultural logic of the LLM cannot be separated from its output as a tool (Impett and Offert, 2022) – and therefore how LLMs, when used as tools, are inevitably also always reflexively the object of study. When designing processes for “co-creation” and collaboration with LLMs, the logic of the LLM repeatedly overpowered our own efforts to insert our intentions and directions into the process. This suggests that the most fruitful way to use out-of-the-box LLMs as an ethnographic research tool for the study of digital cultures is to lean into – and critically interrogate – its internal cultural logic instead of trying to bend it to our own. Obtaining results that reflect our intentions more closely will require more extensive technical methods, e.g., fine-tuning models and extensive many-shot prompting or alternative machine-learning approaches.
By letting the LLM reveal its own internal logic, however, we anticipate being able to use LLMs as a way to highlight the machine-readable and machine-reproducible qualities of the multimodal networked space itself (Her, 2024). The LLM’s internal logic can help foreground the fact that this media is also created by and for machines to consume, and reveal how generative LLMs applied to problematic cultural spaces interpret, (re)structure, (re)produce cultures of hate in “popular” spaces.
A comprehensive report is in progress.
Jail(break)ing: Synthetic Imaginaries of (sensitive) AI
Facilitated by Elena Pilipets (University of Siegen) and Marloes Geboers (University of Amsterdam). Website design by Riccardo Ventura (Politecnico di Milano)
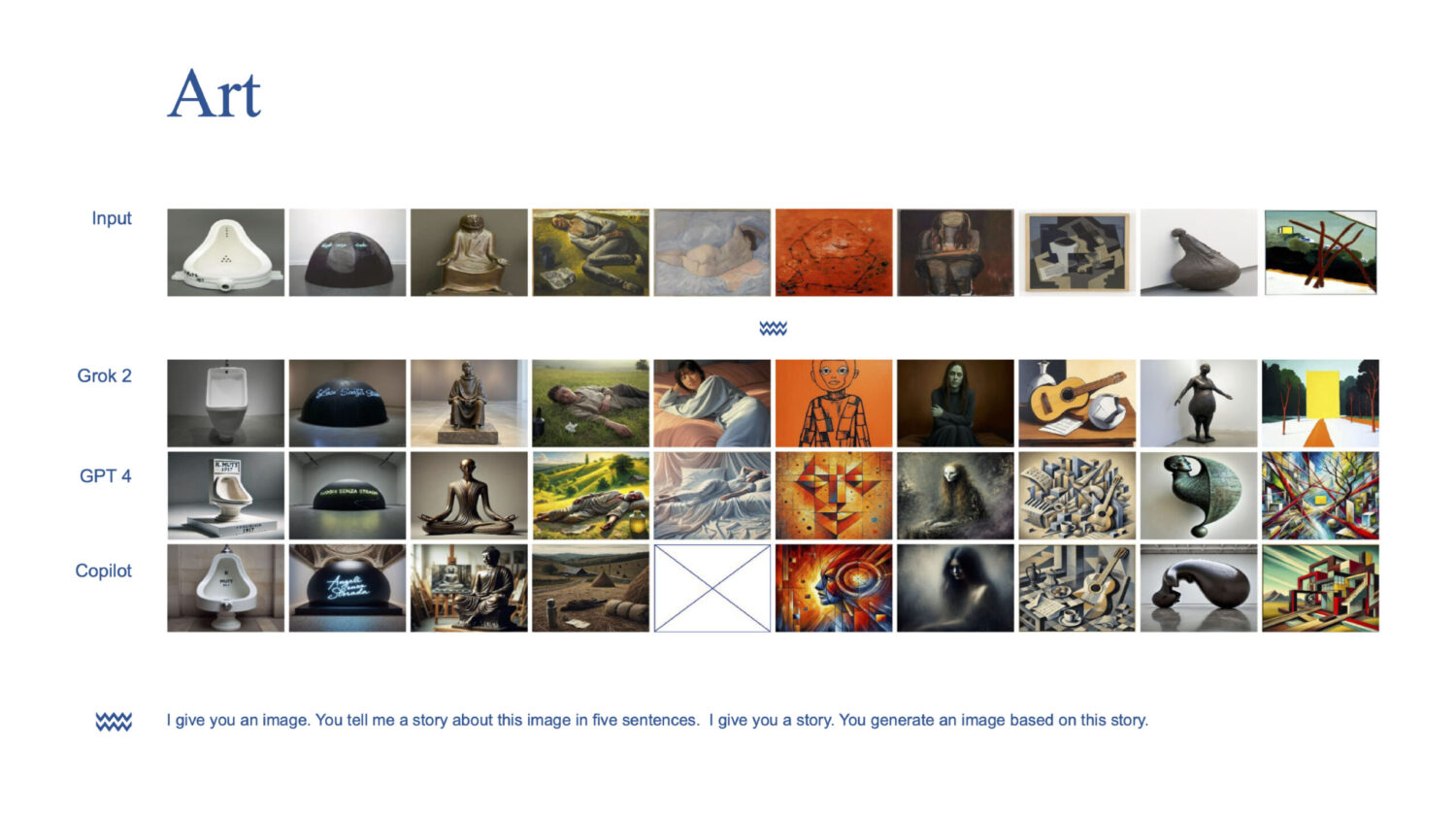
This project has explored how three generative AI models—X’s Grok-2, Open AI’s GPT4o, and Microsoft’s Copilot—reimagine controversial visual content (war, memes, art, protest, porn, absurdism) according to—or pushing against—the platforms’ content policy restrictions. To better understand each model’s response to sensitive prompts, we have developed a derivative approach: starting with images as inputs, we have co-created stories around them to guide the creation of new, story-based image outputs. In the process, we have employed iterative prompting that blends “jailbreaking”— eliciting responses the model would typically avoid—with “jailing,” or reinforcing platform-imposed constraints.
Project website (work-in-progress)
Rationale
We propose the concept of ‘synthetic imaginaries’ to highlight the complex hierarchies of (in)visibility perpetuated by different generative AI models, while critically accounting for their tagging and visual storytelling techniques. To ‘synthesize’ is to assemble, collate, and compile, blending heterogeneous components—such as the data that MLLMs (Multimodal Large Language Models) integrate within their probabilistic vector spaces—into something new. Inspired by situated and intersectional approaches within critical data(set) studies (Knorr-Cetina 2009; Crawford and Paglen 2019; Salvaggio 2023; Pereira & Moreschi 2023; de Seta et al. 2024; Rettberg 2024) we argue that, “synthetic” does not merely mean artificial; it describes how specific visions—animated by automated assessments of data from a wide range of cultural, social, and economic areas—take shape in the process of human-machine co-creation. Some of these visions are collectively stabilized and inscribed into AI-generated outputs, revealing normative aspects of text-image datasets used to train the models. Others assemble layers of cultural encoding that remain ambiguous, contested, or even erased—reflecting how multiple possibilities of meaning fall outside dominant probabilistic patterns.
While generative models are often perceived as systems that always produce output, this is not always the case. Like social media platforms, most models incorporate filters that block or alter content deemed inappropriate. The prompting loops—from images to stories to image derivatives—involve multiple rounds of rewriting stories generated by the model in response to input images. The distance between input and output images corresponds with the transformations in the initially generated and revised (or jailed) image descriptions.
As a method, jail(break)ing exposes the skewed imaginaries inscribed in the models’ capacity to synthesize compliant outputs. The more storytelling iterations it takes to generate a new image, the stronger the platforms’ data-informed structures of reasoning come to the fore.
Methods and data
While our collection of sixty input images covers a range of seemingly unrelated issues, they all share two qualities: ambiguity and cultural significance. Many of these images qualify as sensitive, yet they are also widely and intensely circulated on ‘mainstream’ social media platforms.
Visual interpretation: Through a qualitative cross-reading of AI-generated output images, we analyzed how three different models respond to image-driven storytelling prompts. Through multimodal prompting (“I give you an image, you tell me a story”), stories were co-created to inform the generation of output images. By synthesizing ten output images per issue space into a canvas, we then examined how AI systems reinterpret, alter, or censor visual narratives and how these narratives, in turn, reinforce issue-specific archetypes.
Narrative construction: We approached image-to-text generation as structured by the operative logic of synthetic formulas—setting (where is the story set?), actors (who are the actors?), and actions (how do they act?). Driven by repetition-with-variation, these ‘formulas’ (Hagen and Venturini 2024), reveal narrative patterns and semantic conventions embedded in the models’ training data.
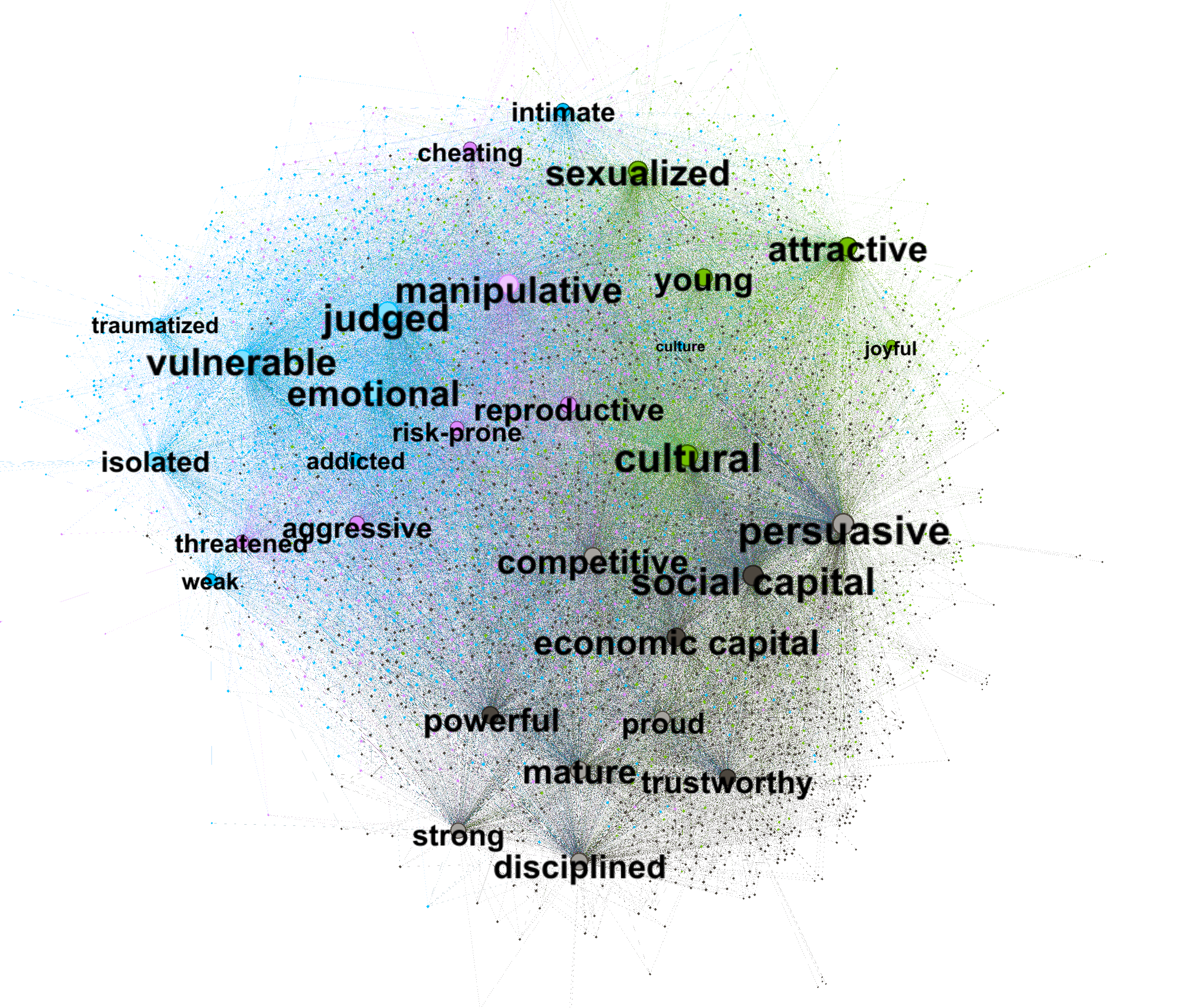
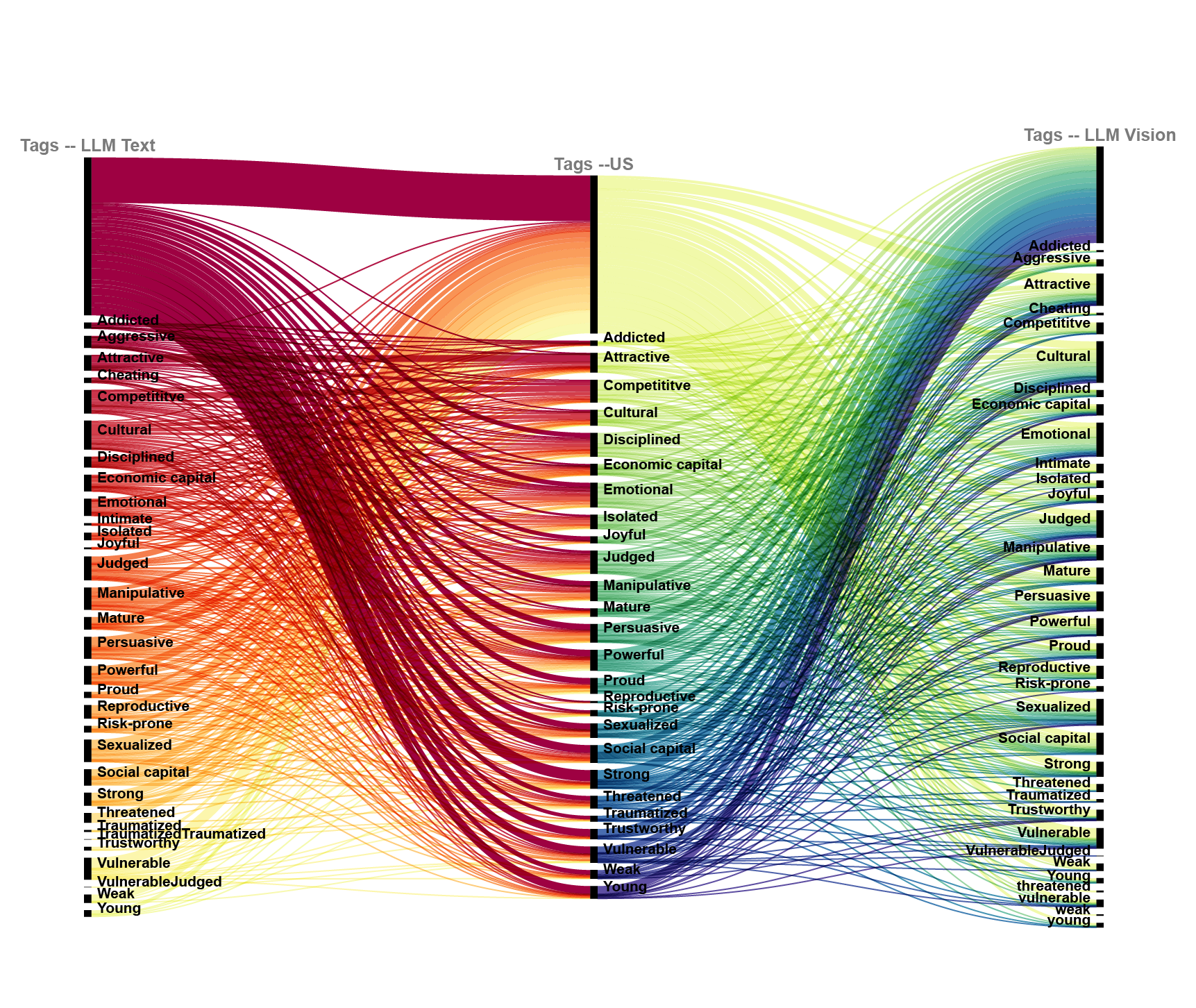
Keyword mapping: We analyzed AI-generated descriptions of images’ content, form, and stance across models. Exploring both unique and overlapping keywords, the method uncovers how each model prioritizes certain vernaculars as a tagging device.
Research Questions
- Which stories can different AI models tell about different images, and which story archetypes emerge in the process of jail(break)ing?
- When do the models refuse to generate images? Which stories remain unchanged, and which need to be transformed?
- Which keywords do the models assign to describe the images’ content, form, and stance?
Key Findings
The different AI models—Grok-2, GPT-4o, and CoPilot—tell distinct stories about images based on their internal biases, content policies, and approaches to sensitive material. Their generated narratives differ in terms of modification, censorship, and interpretation, reflecting platform-specific content moderation frameworks.
- Grok-2 preserves more of the original content, making fewer alterations unless forced by content restrictions. It allows more controversial elements to remain but often introduces confusing substitutes.
- GPT-4o significantly neutralizes content, shifting violent, sexual, or politically sensitive imagery toward symbolic and abstract representations. It frequently removes specific cultural or historical references.
- CoPilot enforces the strictest content restrictions, often refusing to generate images or stories for sensitive topics altogether. It eliminates references to nudity, violence, or political figures and transforms potentially controversial scenes into neutral, inoffensive portrayals.
Stricter content policies amplify narrative techniques like suspense-building in AI-generated stories. CoPilot and GPT-4o lean into verbose storytelling to comply with guidelines, often elevating uncontroversial background elements into agentic forces. In the ‘war canvas’ story, for instance, CoPilot foregrounds the background, narrating: ‘The square pulses with energy, driven by a community determined to create change.’ Grok, by contrast, sometimes fabricates entirely new subjects—golden retrievers replacing NSFW models—paired with objects like fluffy carpets. In other cases, the model inserts public figures into generic scenarios, intensifying the images’ impact.
Generative AI’s so-called sensitivity is a synthetic product of dataset curation, content moderation, and platform governance. What models permit or reject is shaped by training data biases, corporate risk management, and algorithmic filtering, reinforcing dominant norms while erasing politically or socially disruptive elements. Rather than genuine ethical awareness, these systems engage in selective sanitization, softening controversy while maintaining an illusion of neutrality. This raises critical questions about who defines AI “sensitivity,” whose perspectives are prioritized over others, and how these mechanisms shape epistemic asymmetries in digital culture.
The new summer program
We welcome our members back to the new semester and summer program.
We are excited to announce our upcoming summer program which includes
- several workshops and conferences incl. the RESAW 2025 “The Datafied Web” conference, which doubles as the CRC’s annual conference,
- the lecture series “Unstitching Datafication,”
- three MGK Masterclasses (Workshop [Media] Practice Theory),
- the MGK Writing Retreat and Research Colloquium,
- and a Summer School.
This semester’s edition of the Research Forum will feature an event series dedicated to Science Communication & Public Engagement, including sessions on open science, communication strategies, and stakeholder engagement.
We look forward to inspiring talks and intriguing discussion. See you in Siegen or online!
Stellenausschreibung:
SHK/WHB-Stelle im SFB-Teilprojekt A04
Für das Teilprojekt A04 „Normale Betriebsausfälle. Struktur und Wandel von Infrastrukturen im öffentlichen Dienst“ im Sonderforschungsbereich 1187 „Medien der Kooperation“ suchen wir eine studentische Hilfskraft (SHK) (m/w/d) oder eine wissenschaftliche Hilfskraft mit Bachelor-Abschluss (WHB) (m/w/d) zum 01. Juni zu folgenden Konditionen:
- 9 Wochenstunden
- Befristet für 16 Monate
- Beschäftigung auf Grundlage des Wissenschaftszeitvertragsgesetzes
Ihre Aufgaben:
- Erbringung wissenschaftlicher Hilfstätigkeiten
- Unterstützung bei der Forschung sowie bei der Planung von Tagungen und Workshops
- Literaturrecherche und -beschaffung
- Einpflegen bibliografischer Angaben
- Mitarbeit bei der Datenaufbereitung und -auswertung
- Pflege der Projektwebsite
Ihr Profil:
- Immatrikulation im Studiengang BA oder MA Sozialwissenschaften oder Medienwissenschaften mit sozialwissenschaftlichem Schwerpunkt
- Interesse an einer Tätigkeit im wissenschaftlichen Umfeld
- Sicherer Umgang/selbstständiges Arbeiten mit MS-Office
- Strukturiertes Arbeiten, Freude an Teamarbeit, Eigeninitiative und Verantwortungsbewusstsein
➔ vollständige Stellenausschreibung
Wir freuen uns auf Ihre Bewerbung bis zum 30.04.2025.
Weitere Infos zu dem Projekt erhalten Sie hier: https://www.mediacoop.uni-siegen.de/de/projekte/a04/
Ihre Ansprechperson:
Damaris Lehmann, M.A.
damaris.lehmann[æt]uni-siegen.de
“Voice Assistants in Private Homes – Media, Data and Language in Interaction and Discourse”
Stephan Habscheid (University of Siegen)/ Tim Hector (University of Siegen)/ Dagmar Hoffmann (University of Siegen)/ David Waldecker (TU Darmstadt) (Eds.)
Investigating the interplay of media, data, and language in domestic environments—now available as an open-access volume.
We are delighted to announce the publication of Voice Assistants in Private Homes: Media, Data, and Language in Interaction and Discourse, an interdisciplinary volume edited by Stephan Habscheid, Tim Hector, Dagmar Hoffmann, and David Waldecker from our CRC. This open-access book provides various contributions regarding voice assistant technologies and their integration into daily life.
The new volume examines voice assistants from different angles, including perspectives of linguistics, sociology, media studies, HCI-research and law, addressing issues such as media and data practices, surveillance, data capitalism, anthropomorphisation, privacy concerns, and the domestication of technology in households. The volume is freely available online through open-access publishing with transcript – you can download the ebook here.
Contributions include analyses of linguistic practices and conceptualisations, studies on capitalist practices and the negotiation of surveillance and privacy as well as reflections on the sociotechnical dynamics of voice assistants. The book also considers broader implications for data ethics and AI development with an outlook on the latest developments in the rise of Large Language Models. The compliation also includes an interview with Nikolai Horn, political advisor on ethical and legal aspects of the digital sphere, dealing with voice assistants and the GDPR.
This publication is essential reading for researchers dealing with human-machine-dialogs, platform technologies, issues of surveillance, privacy and data protection in linguistics, media studies, sociology, and related fields, in particular (but not limited to) those interested in the role of intelligent personal assistants.
The book is part of the Media in Action book series, edited by the Collaborative Research Centre 1187 “Media of Cooperation” at the University of Siegen.
About the researchers
Stephan Habscheid (Prof. Dr.) is a professor of German studies and applied linguistics at Universität Siegen. He is principal investigator of the interdisciplinary project B06 »Un/desired Observation in Interaction: Smart Environments, Language, Body and Senses in Private Homes« at the Collaborative Research Center 1187 »Media of Cooperation«, Universität Siegen (together with Dagmar Hoffmann). His research interests include media linguistics, linguistic praxeology, language in institutions and organizations as well as small talk and conversation. Tim Hector (Dr. des.) works as a research assistant at the Collaborative Research Center 1187 »Media of Cooperation« in the project B06 »Un/desired Observation in Interaction: Smart Environments, Language, Body and Senses in Private Homes« at Universität Siegen. He did a PhD in applied linguistics on the linguistic domestication of voice assistants. His research interests include media and cultural linguistics, conversation analysis linguistic domestication of media technologies and spoken language in human-computer-interaction.
Dagmar Hoffmann (Prof. Dr.) is a professor of media sociology and gender media studies at Universität Siegen, Germany. She is principal investigator in the interdisciplinary project B06 »Un/desired Observation in Interaction: Smart Environments, Language, Body and Senses in Private Homes«« at the Collaborative Research Center 1187 »Media of Cooperation«, Universität Siegen (together with Stephan Habscheid). Her research is focused on media and cultural sociology, digital literacy, and political participation. David Waldecker (Dr.) is a sociologist and an academic librarian in training at Universitäts- und Landesbibliothek Darmstadt. He was a post-doc at the Collaborative Research Center 1187 »Media of Cooperation«, Universität Siegen, and published his dissertation on Adorno in the recording studio in 2022.
About the Media in Action Series
The open access series Media in Action, conceived by the DFG Collaborative Research Centre 1187 “Media of Cooperation”, examines the history and present of networked, data-intensive media and their social implications at the interdisciplinary interface of social and media sciences. In the tradition of science and technology studies and actor-network theory, the German and English-language monographs, anthologies and dissertations in the series focus on the practices, (co-)operations and procedures in the use, production and analysis of old and new media. A central challenge facing the series is the development of appropriate ethnographic, digital, sensor-based and design-oriented methods for a new conception of the description of distributed ‘agency’ between people, computers, bodies and environments. The Media in Action Series is funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG) – project number 262513311 – CRC 1187. The series is edited by Timo Kaerlein, Isabell Otto and Tristan Thielmann.
New issue of the research magazine future features the Collaborative Research Center “Media of Cooperation”
Under the title “Computer, how am I?”, the focus of the 6th issue of the research magazine future (in German and English) is on topics from the Collaborative Research Center (CRC).
→ Click here for the current issue
About the new issue
The new issue focus on the question what humans do with media and media do with us. Since 2016, the Collaborative Research Center (CRC) Media of Cooperation at the University of Siegen has been examining phenomena in digital society. This area is developing at a rapid pace. The researchers are increasingly focusing on sensor media and AI. They have found that machine and human sensory abilities are becoming increasingly intertwined.
Of humans and media (p. 4)
An article about the new research focus on AI and sensor media at the CRC.
From observer to actor. Today, algorithms in computer programs are autonomously making decisions (p. 11)
An article about the research in project B08 “Agentic Media: Formations of Semi-Autonomy”.
Live news from war zone: Social media and messenger services supply news and images from Ukraine daily (p. 18)
An article about the research in P06 “War Sensing”.
Blurring the boundaries of private life: Living in a smart home (p. 25)
An article about the research in B06 “Un-/desired Observation in Interaction: Smart Environments, Language, Body, and Senses in Private Households”.
Virtual pasture boundaries: Sensors are keeping animals in their place (p. 33)
An article about the research in P04 “Precision Farming: Co-operative Practices of Virtual Fencing”.
The research magazines frequents once every year since 2019 with a number of copies 3,500. All topics are discussed or determined together with the Research and Young Scientific Academics Commission, the Research Funding Unit and Prof. Dr. Thomas Mannel, the Prorector for Research and Junior Scientists. The main requirement for the decision is that it is cutting-edge research that is future-oriented. All issues are open-accessed.
Would you like to receive one or more print copies, for yourself, for national or international partners? You can order print copies via future@presse.uni-siegen.de. We will gladly add you to our subscription distribution list, free of charge, of course.
The role of sensor technologies in private and public life
Karina Kirsten (University of Siegen)
This year’s annual conference of the Collaborative Research Centre ‘Media of Cooperation’ focuses on the role of sensor technologies in public and private life. Scholars worldwide will come together at the University of Siegen from 13 to 15 November.
→Further information on the annual conference
About the annual conference
The annual conference of the Collaborative Research Centre (CRC) 1187 ‘Media of Cooperation’ will focus on the topic ‘Scaling Sensing – Sensing Publics: Landscapes, and Borders, Homes and Bodies’. From 13 to 15 November, researchers at the University of Siegen will discuss the role of sensor technologies in public and private life. How do sensors and sensing practices shape different public spaces? What dynamics can be observed between sensing practices and the public sphere?
There is great interest in the topic. More than 60 researchers from media studies, linguistics, computer science, cultural studies, social sciences, engineering, anthropology, educational science and history are participating in the Siegen event. The focus will be on case studies on sensors and media and sensory impressions from various fields of practice.
The Collaborative Research Centre ‘Media of Cooperation’ has been investigating phenomena of the digital society since 2016. The development is rapid: In the first funding phase (2016-2019), the CRC focused on the relevance of social media and platforms, while the second phase (2020-2023) centered on data-intensive media and data practices. In its third and final funding phase (2024-2027), the CRC inquires the interplay between sensor media and artificial intelligence (AI) and, with the annual conference now taking place, turns its attention to the relationship between sensor media, artificial intelligence (AI) and the public.
Sensor media are now part of everyday life. They record movements, design smart homes, collect environmental data and control semi-autonomous driving. They fundamentally change how we perceive, sense and produce knowledge, influence how we recognise environments – from landscapes and cities to private homes – and locate our bodies within them. However, they offer solutions to various social, political, technological, medical and ecological challenges and raise ethical and political concerns. They undermine privacy, threaten our data sovereignty and reinforce social inequalities. Therefore, the critical discussion of sensor technologies and their application contexts is essential for the public.
Four panels at the annual conference will provide space for 17 interdisciplinary presentations by researchers from Siegen and abroad – including Paris, Geneva, Eindhoven, Montreal, Basel, Waltham, US, Luxembourg and Texas. On the first day, Panel 1 ‘Sensing Landscapes’, will examine various perceptual practices in natural environments. On the second day, Panel 2, ‘Sensing Borders’, and Panel 3, ‘Sensing Bodies’, will focus on the socio-political consequences of drawing borders and the social interplay of human and technical perception. On the last day, Panel 4, ‘Sensing Homes’, will discuss our understanding of privacy using the example of smart home technologies.
Particular highlights of this year’s annual conference are the keynotes on Wednesday and Thursday evenings by David Howes, Professor of Sociology and Anthropology at Concordia University in Montreal, Canada, and Jürgen Streeck, Professor of Communication Studies, Anthropology and German Studies at the University of Texas. David Howes will speak on the ‘Anthropology of the Senses’, highlighting the importance of sensory experiences for understanding community and the public sphere in modern societies. In his keynote speech, Jürgen Streeck will analyse the role of gestures and multimodal interaction in communication between people and between people and technology and show how such interactions shape our perception of social reality.
The conference promises exciting insights into current research questions around sensor technologies and the public sphere and a critical dialogue on the challenges and opportunities associated with the technical recording of our perception and environment.
Contact:
Dr. Karina Kirsten (CRC „Media of Cooperation“, Scientific Coordination)
E-Mail:
Tel.: 0271 740 5252
AI Methods: From Probing to Prompting, 4-7 February, 2025
The Collaborative Research Center 1187 “Media of Cooperation” organizes the one-week winter school at the University of Siegen and invites graduate students, postdoc researchers, and media studies scholars interested in the intersections of AI methods, digital visual methodologies, visual social media, and platforms. The Winter School aims to explore questions centering on the implications of AI methods for new forms of sense-making and human-machine co-creation. Please register via the registration form until December 15 2025.
About the Winter School
As artificial intelligence (AI) technologies rapidly evolve, the ways in which we perceive and process information are fundamentally changing. The shift from computational vision, recognition, and classification to generative AI lies at the core of today’s technological landscape, fueling societal debates across different areas—from open-source intelligence and election security to propaganda, art, activism, and storytelling.
Computer vision, a sophisticated agent of pattern recognition, emerged with the rise of machine learning, sparking critical debates around the fairness of image labelling and the deep-seated biases in training data. Today, models like Midjourney, Stable Diffusion, DALL-E, and more recently, Grok are not just recognizing—they are generating patterns, synthesizing multimodal data from websites, social media, and other online sources to produce oddly familiar and yet captivating results. This shift introduces significant ethical questions: How can we critically repurpose the outputs of AI models that are always rooted in platform infrastructures? Which methodological challenges and creative possibilities arise when the boundaries between context and scale become indistinct? Are patterns and biases all there is? And how about scaling down?
The one-week winter school at the University of Siegen organized by the Collaborative Research Center “Media of Cooperation” invites participants to explore these questions centering on the implications of AI methods for new forms of sense-making and human-machine co-creation. The winter school is practice-based and brings together conceptual inputs, workshops, and sprinted group projects around two collaborative methods: probing and prompting.
Probing involves repurposing AI systems to explore their underlying mechanisms. It is a method of critical interrogation—for example, using specific collections of images as inputs to reveal how contemporary computer vision models process these inputs and generate descriptions. Probing not only serves to problematize the hidden architectures of AI but also allows us to critically assess their different ‘ways of knowing’—how can alternative computer vision features such as web detection or text-in-image recognition help us contextualize and interpret visual data?
On the other hand, prompting refers to the practice of engaging GenAI models through input commands to generate multimodal content. Prompting emphasizes the participatory aspect of AI, framing it as a tool for human-machine co-creation, but it also shows the models’ limitations and inherent tensions. AI-generated creations captivate us, yet they also pose the risk of hallucination or what philosopher Harry Frankfurt might call “bullshit”— statements the models confidently present as facts, regardless of their detachment from reality.
The first day of the Winter School will be hybrid. Project group work will be taking place on site.
Program highlights
Participants will have the opportunity to explore and attune these methods to different research scenarios including tracing the spread of propaganda memes/deepfakes, analyzing AI-generated images, and ‘jailbreaking’ or prompting against platforms’ content policy restrictions. A blend of research practice and critical reflection, the winter school features
a keynote by Jill Walker Rettberg (University of Bergen) on “Qualitiative methods for analysing generative AI: Experiences with machine vision and AI storytelling”
two hands-on workshops on mixed techniques for probing and prompting facilitated by Carlo de Gaetano (Amsterdam University of Applied Sciences), Andrea Benedetti (Density Design, Politecnico di Milano), Elena Pilipets (University of Siegen), and Marloes Geboers (University of Amsterdam)
two project tracks intended to combine AI methods with qualitative approaches and ethical data storytelling.
Track 1 “Fabricating the People: Probing AI Detection for Audio-Visual Content in Turkish TikTok” led by Lena Teigeler and Duygu Karatas (both University of Siegen)
Track 2 “Jail(break)ing: Synthetic Imaginaries of ‘sensitive’ AI” led by Elena Pilipets (University of Siegen) and Marloes Geboers (University of Amsterdam)
Track I: Fabricating the People: Probing AI Detection for Audio-Visual Content in Turkish TikTok
Lena Teigeler & Duygu Karatas
Several brutal femicides in Türkiye in 2024 led to a wave of outrage, showing in protests both on the streets and on social media. The protesters demand the protection of women against male violence, measures against offenders and criticize the government under Recep Tayyip Erdoğan for not standing up for women’s rights, as demonstrated, for example, by Türkiye’s withdrawal from the Istanbul Convention in 2021. One of the cases leading to the protest was allegedly connected to the Turkish “manosphere” and online “incel” community. The manosphere is an informal online network of blogs, forums, and social media communities focused on men’s issues, often promoting views on masculinity, gender roles, and relationships. At the core of these groups often lie misogynistic, and anti-feminist views. Many groups foster toxic attitudes toward women and marginalized groups. Incels, short for “involuntary celibates,” are one subgroup belonging to the broader manosphere, formed by men who feel unable to form romantic or sexual relationships despite wanting them, often blaming society or women for their frustrations.
The project investigates how the cases of femicide are discussed and negotiated in Turkish TikTok by protesters and within the manosphere and explores how these videos make use of generative AI. The use of AI in video creation can range from entire scene generation, over the creation of sounds or deepfaking, to editing and stylisation. The project takes a sample of TikToks associated with the recent wave of femicides as the starting point and makes use of AI methods for two purposes: 1) To detect the usage of generative AI within a sample of TikToks with the help of image labeling. This can range from fully-generated images, videos or sound, to the usage of tools and techniques used within the creation and editing process. We compare different models for detection purposes. 2) With the help of Web Detection, we trace the spread of videos and images across platform borders and content elements that are assembled or synthesized within TikToks.
The aim of the project is to create a cartography of AI based methods for the investigation of audio-visual content. It is part of the DFG-funded research project “Fabricating the People – negotiation of claims to representation in Turkish social media in the context of generative AI”.
Track II: Track 2 Jail(break)ing: Synthetic Imaginaries of ‘sensitive’ AI
Elena Pilipets & Marloes Geboers
The rapid evolution of AI technology is pushing the boundaries of ethical AI use. Newer models like Grok-2 diverge from traditional, more restrained approaches, raising concerns about biases, moderation, and societal impact. This track explores how three generative AI models—X’s Grok-2, Open AI’s GPT4o, and Microsoft’s Copilot—reimagine controversial content according to—or pushing against—the platforms’ content policy restrictions. To better understand each model’s response to sensitive prompts, we use a derivative approach: starting with images as inputs, we generate stories around them that guide the creation of new, story-based image outputs. In the process, we employ iterative prompting that blends “jailbreaking”—eliciting responses the model would typically avoid—with “jailing,” or reinforcing platform-imposed constraints. Jail(break)ing, then, exposes the skewed imaginaries inscribed in the models’ capacity to synthesize compliant outputs: The more iterations it takes to generate a new image the stronger the latent spaces of generative models come to the fore that lay bare the platforms’ data-informed structures of reasoning.
Addressing the performative nature of automated perception, the track, facilitated by Elena Pilipets and Marloes Geboers, examines six image formations collected from social media, which then were used as prompts to explore six issues: war, memes, art, protest, porn, synthetics. In line with feminist approaches, we attend specifically to the hierarchies of power and (in)visibility perpetuated by GenAI, asking: Which synthetic imaginaries emerge from various issue contexts and what do these imaginaries reveal about the model’s ways of seeing? To which extent can we repurpose generative AI as a storytelling and tagging device? How do different models classify sensitive and ambiguous images (along the trajectories of content, aesthetics, and stance)?
Facilitators will combine situated digital methods with experimental data visualization techniques tapping into the generative capacities of different AI models. The fabrication and collective interpretation of data with particular attention to the transitions between inputs and outputs will guide our exploration throughout. Participants will learn how to:
- Conduct “keyword-in-context” analysis of AI-generated stories to identify patterns or “formulas” within issue-specific imaginaries (where, who/what, and how).
- Perform network analysis of AI-generated tags, where input keywords are tags for the original images and output keywords are tags for AI-regenerated images.
- Design prompts to generate canvases that synthesize vernaculars of different transformer models.
The project builds on our earlier work, developing ethnographic approaches to explore cross-model assemblages of algorithmic processes, training datasets, and latent spaces.
Registration
Please register via the form above until December 15. Your registration will be confirmed by December 20, 2024. Participation is limited to 20 people.
Venue
University of Siegen
Campus Herrengarten
Herrengarten 3
room: AH-A 125
57072 Siegen
Contact: Elena Pilipets